Ashima Sharda Mahindra • 02 Apr 2025
Fuller House star Dave Coulier Finishes Chemotherapy to Treat Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
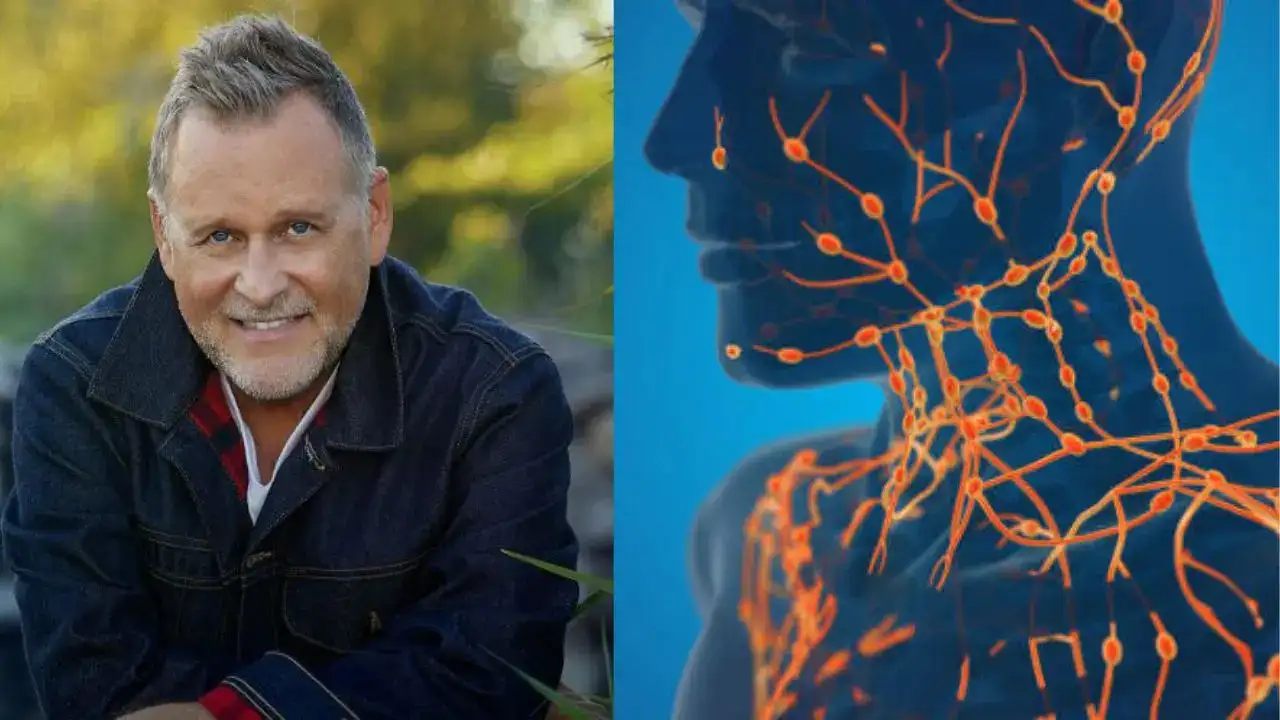
Coulier said a recent biopsy on a lymph node in his neck showed “no sign of cancer'
Fuller House star Dave Coulier hopes he can get past cancer as he completes his chemotherapy sessions for stage 3 non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Coulier said a recent biopsy on a lymph node in his neck showed “no sign of cancer,” and he’s now waiting for the results of an additional CAT scan to see whether his illness “will be in the rearview mirror.”
Speaking to Parade in an interview, the 65-year-old actor also added that a PET scan he underwent halfway through his treatment did not show any cancer cells.
Coulier had been diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma in November 2024 and since then has undergone six rounds of chemotherapy. It is a type of blood cancer that starts in the lymphatic system. The lymph system is part of the immune system and helps protect your body from infection and disease. “Melissa (wife) and I waited for a week to get the biopsy results back, and there is no sign of cancer,” he told Parade. “One of the few times in my life when ‘zero’ has been a great number to hear.”
Coulier's symptoms
Couli who plays Uncle Joey in both the original and the reboot, said he first noticed symptoms after coming down with a cold. He found a golf-ball-sized lump in his groin within a week of feeling sick. After starting with the treatment post his diagnosis, Coulier said he began feeling neuropathy, nausea, dizziness, and “chemo brain" and found himself in a mental fog.
“I was in such a daze when I walked out of the hospital; my wife looked at me when we got in the car, and she goes, ‘We forgot to ring the bell,’” he said.
What is non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a group of blood cancers that develop in your lymphatic system. It is one of two types of lymphoma - cancers that start in white blood cells and are important for your immune system.
With non-Hodgkin lymphoma, genes inside B lymphocytes - the B cells or T lymphocytes or the T cells—mutate at some point in your lifetime. The abnormal lymphoma cells usually form in your lymph nodes and form tumours. But they can also be in other lymph system organs, like your thymus or spleen, and even other places.
Experts say today most people with non-Hodgkin lymphoma are living longer than ever due to new treatments. In some cases, treatments even cure the condition.
Signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
The most common symptom of non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a painless swelling in your neck, armpits, or groin. It happens when your lymph nodes get swollen in those areas. Other signs and symptoms include:
- Persistent fatigue
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Breathlessness
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Feeling full despite not eating much
- Unexplained fever
- Drenching night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
What causes non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Doctors say non-Hodgkin lymphomas form when your body produces too many lymphocytes, which include B cells, T cells, or even rarely the natural killer cells. A few acquired genetic mutations that affect lymphocyte growth play an important part in the process.
When lymphocytes mutate, they begin to multiply and eventually become tumours that start in your lymph nodes. As your lymphatic system touches nearly every part of your body, non-Hodgkin lymphoma often spreads to other lymph organs.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world.